Guide to Online Payment Method Types for eCommerce Businesses
Table of Contents

We help businesses accept payments online.
The rise of new online payment methods across the globe has created new opportunities, as well as new problems for EC site owners. In the old days, payment by credit card or COD was sufficient. But now, users expect to use a diverse range of payment methods that vary across each country or market. Each market has its own preferences and demographic groups.
In this article, we guide you through all the payment options available, explain why it matters which ones, and how many you should offer. We also provide important payment method tips for your eCommerce business.
Understanding Payment Options

These are the payment methods that eCommerce companies tend to offer:
- Cards
- Cash
- Digital wallet
- Bank transfer
- Buy now, pay later (BNPL)
- Convenience store
- Carrier billing
We will cover and compare them in depth shortly.
But first, it’s important to understand that there is no single best payment method for eCommerce businesses.
Influenced by consumer habits, internet infrastructure, government initiatives, and other factors, each part of the world has certain preferences regarding payment methods. Hence, all the listed options have their time and place.
This graph illustrates the breakdown of payment methods as used by region:
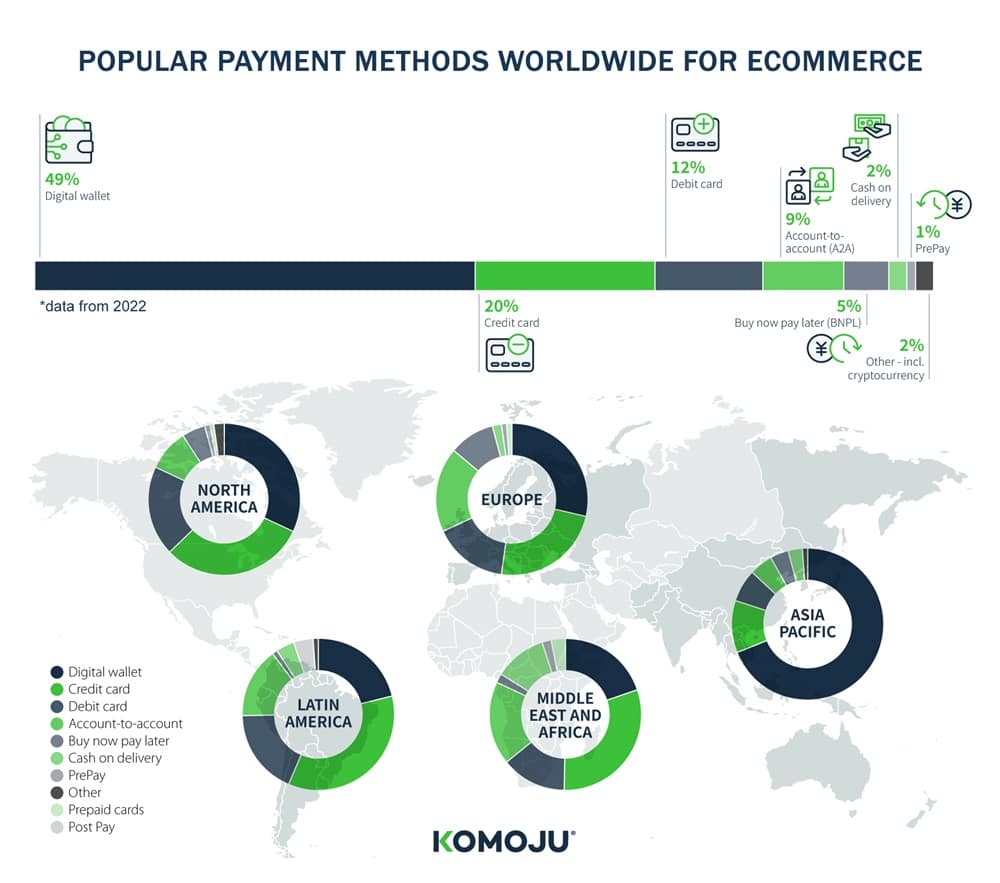
Even at a high level, the differences between regions are obvious.
Europe payment methods are spread between credit and debit cards, digital wallets, account-to-account transactions, and buy now pay later (BNPL).
Asia Pacific strongly prefers digital wallets, while other methods are used far less. Digital wallets account for almost three-quarters of the region’s total transaction value according to Statista’s data.
Yet, even with this seemingly straightforward initial split in the Asia Pacific, the picture becomes more complicated when we look at payment preferences in individual countries.
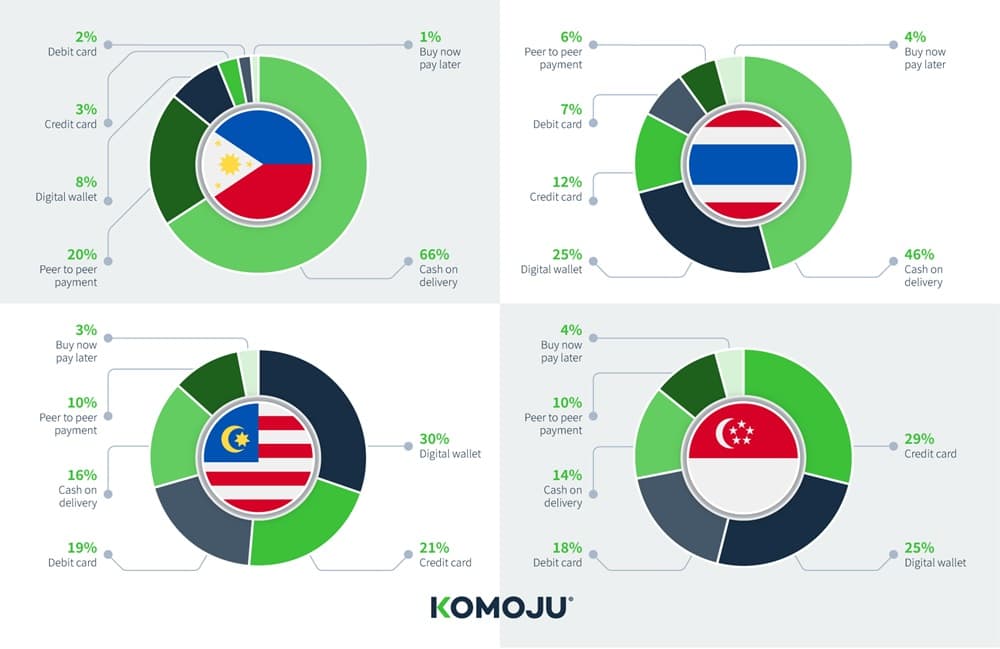
Here is a breakdown of popular payment options in prominent Asia Pacific eCommerce markets:
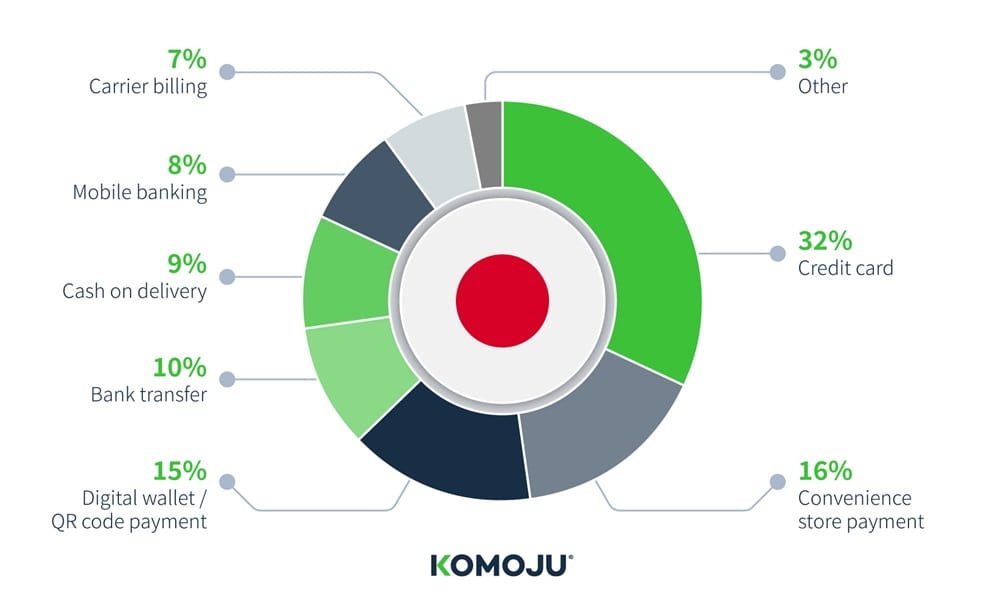
Japan:
Payment methods in Japan show a strong preference for credit cards at 40.2% and a significant adoption of digital wallets at 22.6%. Other payment methods such as carrier payments, prepaid cards, and debit cards also contribute to the diverse financial ecosystem in Japan.
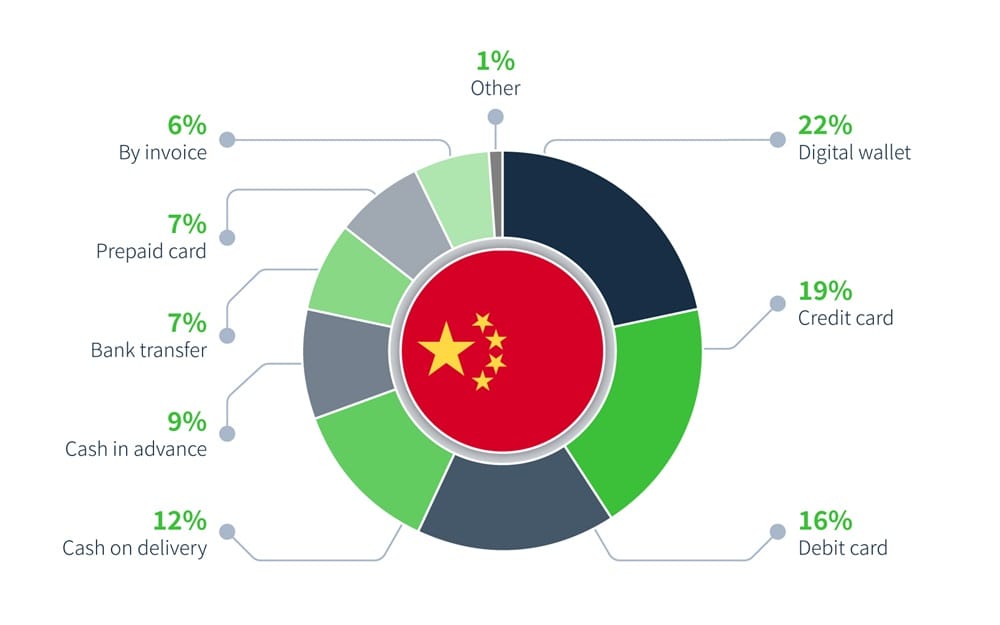
China:
China’s payment method distribution indicates a prominent reliance on digital wallets at 21.9%, with credit and debit cards also playing major roles at 19% and 16.2% respectively, alongside traditional methods like cash on delivery and bank transfers.
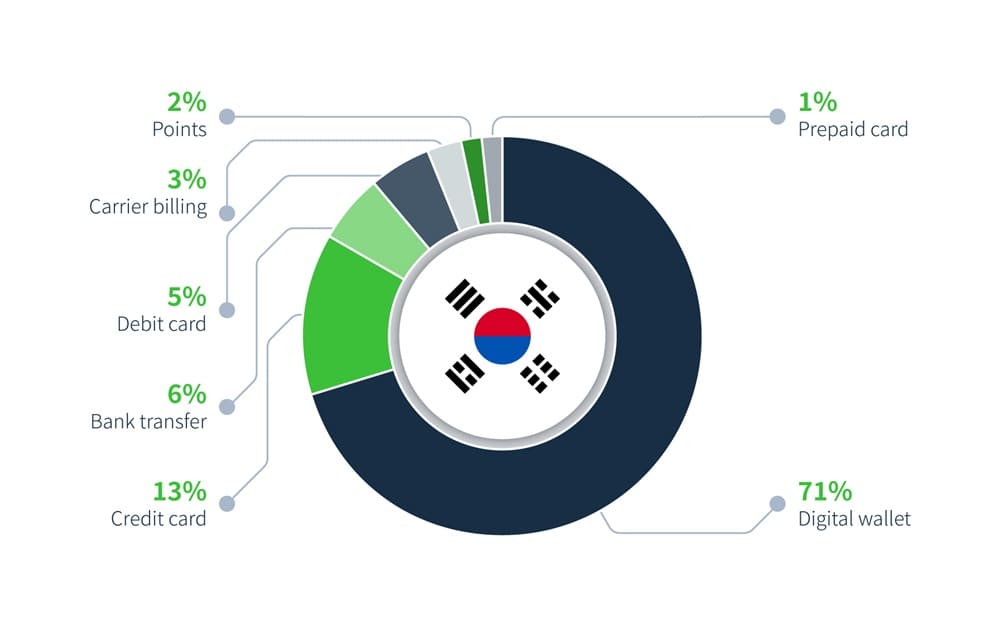
South Korea:
South Korea’s payment method preferences reveal 70.5% reliance on digital wallets, alongside significant figures for credit cards, debit cards, and bank transfers, showcasing the country’s advanced digital finance landscape.
Southeast Asia:
Payment methods in Southeast Asia display a dynamic and varied landscape, as shown in the infographic. Cash on delivery remains dominant in the Philippines and Thailand, while Malaysia and Singapore are witnessing a significant rise in digital wallet usage, signaling a shift towards digital payments across the region.
Another less obvious but crucial note: even when countries favor the same payment method category, the actual channel or brand can differ. This is most notably the case with digital wallets.
For example, South Korea’s favorite digital wallets are Naver and KakaoPay, while China uses Alipay, WeChat Pay, and UnionPay the most.
If you’re targeting both markets, it is best to offer at least some of their local favorites.
We will explore why offering various local payment methods is worth investing the time and money to implement before listing your options.
The Benefits of Providing Various Payment Methods
Here are some concrete reasons to offer a range of trusted local payment methods:
- Increases your market penetration – opens your door to all customers in your target region by ensuring at least one of their trusted payment methods is available
- Facilitates trust with customers and boosts their satisfaction – they feel valued and respected because your business is accommodating their preferences.
- Provides a smooth user experience – customers can use their most convenient payment option, and this positive experience makes them more likely to return to your company
- Removes obstacles at the checkout and decreases abandoned shopping cart rates – lack of unpleasant surprises at the final step increases the chance of customers completing the purchase
- Improves payment security by reducing the risk of fraud – companies can choose payment methods with stronger customer authentication processes. With the losses to payment frauds rising globally, security is an increasingly important consideration
Types of Payment Methods

Here’s what information to expect regarding each payment method type below:
- An overview
- The pros and cons from your perspective as a seller
- The pros and cons from your customers’ perspective
Cards
There are three types of cards customers use:
- Credit card
- Debit card
- Prepaid card
Despite belonging to the same category and coming in the same plastic card form, these three have fundamental operational differences.
Credit cards offer an individual a set amount of credit they can borrow for purchases. Importantly, this sum is separate from the funds the person owns (their debit balance). With a credit card purchase, the credit card company covers the costs until the repayment date, effectively delaying when the buyer spends owned funds for each purchase. Over time, using a credit card builds a credit history. A good credit history can later be useful for larger purchases, serving as proof that the individual is financially responsible and stable.
Credit cards are a mainstream payment method because they allow users to shop as needed instead of waiting for payday each month and potentially missing good deals. An important note is that each credit card transaction typically charges a small fee from the merchant. This is why some stores set a minimum spend amount to enable credit card payment.
Debit cards provide no credit. Instead, they allow users to draw money and make purchases strictly from and up to their account balance. If the user attempts to draw or use more money than they have available in the account, the request is rejected and the bank may charge overdraft fees.
Debit cards are widely used. They promote responsible spending without the risk of incurring debt. On the downside, debit cards don’t build a credit score. Although their fraud protection is weaker than credit cards, they’re usually secure.
Prepaid cards are some of the safest payment methods around. Much like prepaid phones, they require a sum of money to be put on the card for use in advance. The customer can only use up to the amount they put on the card. Prepaid cards are often used for specific purchases and purposes only. If stolen, the damage is minimized to the prepaid funds because the card becomes useless after the money is spent.
Most online businesses that accept debit cards, accept prepaid cards too, as these are often backed by major card networks such as Visa, Mastercard, or AmericanExpress. A downside of prepaid cards is that they don’t help to build a credit score. They can also cost more than it seems. For example, fees may be charged for inactivity, declined transactions, or closing the account.
| For sellers | For buyers |
Pros of credit cards | ● Universally used across the globe ●Easy to integrate with minimal localization ● Typically secured against fraud | ● Build a credit score that is useful for big future purchases ● Flexible, can be used at any time up until a set limit is reached ● Delay the use of the person’s owned funds ● Savings opportunities via airline miles and other rewards |
Cons of credit cards | ● Charge a processing fee for each transaction | ● Risk of overspending ● Can incur credit card debt if overextended ● The setup process can be complicated and requires a bank visit ● May charge processing fees ● High interest rates on unpaid balances (15%-25% APY) ● May hurt credit score if not paid regularly |
Pros of debit cards | ● Popular around the globe ● Easy to integrate with minimal localization | ● No risk of debt because it only allows spending up to account balance ● If a purchase cost exceeds the balance, it will be rejected ● No transaction or annual fees if there’s some money in the account ● No interest ● Easy to manage |
Cons of debit cards | ● May charge processing fees ● Limited fraud protection | ● Don’t build credit history ● May charge processing fees for failed purchase attempts due to insufficient funds ● Requires bank setup ● Can’t cross the owned balance limit even for emergencies ● Less safe than credit cards as the money comes from the account holder |
Pros of prepaid cards | ● One of the safest payment methods ● Widely used around the world ● Easy to integrate, just like debit cards | ● Secure, and limits the damage in case of fraudulent use ● Promotes responsible spending ● No risk of debt |
Cons of prepaid cards | ● Limited fraud protection | ● Must be charged before using ● Don’t help build credit score ● In certain cases, can only be used for specific brand or category, such as with gift cards ● Often includes additional fees |
Cash
Although online payment methods are becoming increasingly popular and innovative, cash remains a trusted, secure, and widely used payment method. This is especially true for some countries like the Philippines, where cash on delivery is the most used payment method, or Japan, where convenience store payment is a popular option.
Banknotes and coins are accessible to everyone. This is especially crucial in regions with low card penetration where many customers don’t have any other payment options besides cash.
Cash-on-delivery is also gaining popularity because it allows customers to inspect their order before paying. It gives them that final boost of buyer confidence which they may lack online, especially if they’re new to online shopping.
Research from 2021 in Europe and the Americas backs it up: 44% of people would shop online more if cash payments were accepted, and 47% would prefer this payment method overall.
| For sellers | For buyers |
Pros | ● No transaction fees ● Facilitates customer confidence and trust ● Available to all customers | ● No fees apart from ATM withdrawal fee ● No setup procedure ● No risk of fraud ● Accessible to anyone ● Enables customers to inspect products before buying |
Cons | ● Potential losses if the customer decides not to proceed with purchase ● Security risk, as cash can be stolen from couriers or lost ● Collecting and managing cash can be tedious ● Currencies differ between countries | ● Doesn’t build credit score ● No digital record of spending ● Must be home at delivery time to pay |
Digital Wallet
Digital wallets such as Amazon Pay, Apple Pay, or Google Pay, are applications that can store information about multiple debit or credit cards in one account. They remove the need to enter this information for each online payment.
Some, like PayPal, can store money on the app and issue their own cards. Others only serve as a convenient bridge between the sender’s and recipient’s accounts. Digital wallets can be used via any device, making them suitable for mobile payments and very convenient.
Digital wallets are the most popular online payment method worldwide since 2022, and this share is set to surpass 54% by 2026.
Clearly, this is a payment option eCommerce businesses need to offer worldwide. However, managing digital wallets can be more complicated than some other payment methods. This is because there are so many different digital wallets to choose from. Their processes, fees, user experience, and customer support levels vary – just like their user bases.
As we mentioned earlier, each region has preferences towards particular, usually local apps. Offering multiple choices is crucial for a smooth and localized checkout process. The most practical way to manage this is using a payment service provider.
| For sellers | For buyers |
Pros | ● The widest user base worldwide ● Accessible to users regardless of their device choice ● Often secure with multiple layers of authentication | ● Mobile-friendly and convenient to use ● Often secure with no need to enter card information for each payment ● Quick |
Cons | ● Every region has different digital wallet preferences ● Complicated to manage without a payment service provider ● Varying levels of security between different wallets | ● Not as widely accepted as cards ● Varying policies and protection levels |
Bank Transfer
Wire and bank transfer (commonly referred to as Automatic Clearing House or ACH payment in the US) both include sending money electronically from one bank account to the other. One of the main differences between them is that a wire transfer works both nationally and internationally, while ACH typically includes domestic transactions only.
The advantages of bank transfers include very high security, lack of processing fees, and the ability to set up recurring payments. ACH also takes longer to process than wire (between 1-3 days).
Wire transfers are usually processed within 24 hours, but each transaction comes with a fee. It’s less secure than ACH, can’t be reversed, and doesn’t support recurring payments.
Bank transfers are often complicated for users to set up because of all the security layers. But after that, they’re easy to use via online banking or mobile banking.
| For sellers | For buyers |
Pros | ● High security ● Ability to set up automatic recurring payments ● No transaction fees for bank transfers ● Widely used ● Fast payment processing for wire | ● High security ● Useful for more important and expensive purchases ● Easy to use once set up via online banking ● Can be accessed via smartphone |
Cons | ● Can be expensive to manage, especially wire ● May charge transaction fees | ● Wire transfers can’t be reversed ● The setup process can be complicated |
Buy Now, Pay Later (BNPL)
Buy now, pay later allows customers to pay for their purchase in installments over time instead of charging them a lump sum. The idea is to make more expensive purchases accessible and affordable by breaking the total cost into manageable pieces. With BNPL, customers can receive and use the products without waiting until they accumulate enough money to pay for them.
Companies commonly include a small interest rate, so the final cost with BNPL may be higher than it would have been if paid all at once. But even so, this payment method can help customers save money in the long run.
Without BNPL, customers’ pool of options is often limited to the products they have the funds to purchase in full. This sometimes means settling for cheap products and repurchasing them often. These costs add up over time and far surpass the cost of more expensive alternatives.
With BNPL, customers can get sustainable, durable items that cost less to regularly replace.
BNPL has been soaring in recent years, especially in Europe. In Denmark, accepting installment-based payments for at least 50% of the cost is mandatory for eCommerce businesses.
Interestingly, this payment method is particularly popular with younger customers. Generation Z has shown the highest average BNPL monthly debt of 80% in this UK study.
| For sellers | For buyers |
Pros | ● Expands the customer base for more expensive products ● Boosts buyer confidence as the upfront cost is smaller ● Total product cost is often higher due to interest ● Popular with younger audiences | ● Makes expensive products accessible ● Eliminates the wait time before receiving and using the item ● Widens the pool of product options to choose from |
Cons | ● Delayed payment | ● The full cost of products is higher due to interest |
Convenience Store
Convenience store payment is the most popular alternative to cards in Japan. With over 40,000 convenience stores (konbini) open across the country, there’s one at nearly every corner and they’re open 24 hours, 7 days a week.
Konbini payments allow companies to access the entire population in Japan. This includes those who don’t have or want to use cards and abandon shopping carts if no other payment options are available.
Convenience stores enable customers to pay in cash on the spot for a small fee. Unlike cash-on-delivery, convenience store payment doesn’t require customers to wait at home to pay. The delivered items are held by the konbini, allowing customers to choose a convenient time to pick them up.
Additionally, customers may stay anonymous and avoid the security risks of putting personal data online. If you plan to expand to Japan eCommerce, convenience store payment is an important payment method to include.
| For sellers | For buyers |
Pros | ● Access to the entire Japanese eCommerce market ● Essential for building a Japanese customer base ● Very secure | ● Convenient 24/7 access for anyone ● No waiting time to pay, unlike cash-on-delivery ● Doesn’t require trusting websites with personal data ● Doesn’t require a bank account or digital literacy |
Cons | ● Highly localized, doesn’t apply globally | ● Charges a small transaction fee ● Doesn’t build credit score |
Read the latest whitepaper about an essential Japanese local payment method, Konbini Payments.
Carrier Billing
Carrier billing is a mobile-based online payment method that charges purchase costs directly to the user’s mobile bill. It doesn’t require customers to have a bank account or include many personal details associated with other traditional payment methods. Carrier billing is known for its smooth user experience, convenience, and accessibility.
This payment method is generally not intended for purchasing physical goods. It’s typically used for virtual goods and specific transactions, such as transportation ticket payments or city parking.
| For sellers | For buyers |
Pros | ● Expands the consumer base to include those without bank accounts ● Popular among younger generations | ● Easy to use ● Secure ● Doesn’t require a bank account ● Works via smartphone |
Cons | ● Delayed payment depending on when the phone bill is charged | ● Usually can’t be used for physical goods ● Not widely supported |
Tips for Choosing the Right Payment Methods for Your Business

Below are some key points that will help you choose which payment type to use for your business.
1. Diversify Payment Options
Most eCommerce companies accept a range of payment options. Expanding yours is the minimum you have to do to stay competitive, especially if you’re selling on several different markets.
2. Figure Out Your Payment Processing Logistics
Payment processing is the technical part of accepting online payments.
These are the three terms you must understand to pick the right payment processing method for your business:
- Merchant account – When a customer makes a purchase, this is where the funds go until they are officially settled and approved for use by the customer’s bank. From there, the funds proceed to your account. Merchant accounts are necessary to accept any sort of online payment. They can be personal (used only by your business) or aggregate (shared between several businesses).
- Payment gateway – This is the technical service of collecting the customer’s payment data required to make the transaction. Some payment methods like PayPal come with this service. For others, you may need a third-party gateway or a payment services provider.
- Payment services provider (PSP) – This is a provider or service that acts as an intermediary and integrates multiple payment methods and all the logistics into one platform. PSP comes with an aggregate merchant account and dedicated customer service. This makes the payment setup process quick and easy for eCommerce businesses.
As an eCommerce business, you have two options. You can either set up a private merchant account and manage your own logistics, or outsource them to a third party.
Managing logistics yourself can be a viable option if you sell in one country or offer a few payment methods only. A dedicated merchant account with a local bank can be more secure because there are no other merchants in the pool whose activity can influence your company. However, the setup alone can be complicated and take weeks. Dedicated merchant accounts also aren’t suitable for international payments. As such, they could hold back your expansion and require more man hours to manage.
This isn’t an issue if you partner with a payment services provider because all your payments are integrated into a single subscription – including payment channels you might add in the future.
Partnering with a PSP means that payment management is taken care of for you. This option is more sustainable long-term: it doesn’t create extra work on your end when you scale your business, and it supports international payments.
Here are some additional PSP perks for your consideration:
- Consultation to help you identify the best payment options for your specific context and business goals
- Unbiased expert knowledge about local payments to help with future planning
- Uncomplicated setup process, without the need for a dedicated merchant account
(and the bureaucracy that comes with it)
3. Prioritize Security
It’s in everyone’s best interest to ensure transactions are as safe as possible. Here are some practices that make your online store and payments safer:
- Use a secure eCommerce platform
- Require multi-step authentication
- Authenticate user identities and encrypt data with SSL certificates
- Use a virtual private network (VPN)
- Educate customers never disclose sensitive information via email, chat, or SMS
- Train employees to keep your company and customers safe
- Set strong account password requirements
- Meet compliance requirements for all payment providers
Following these steps helps prevent data breaches and related losses, protects customers, and builds trust in your brand.
4. Assess Costs and Resources
Upfront and setup costs, transaction fees, hidden fees, chargeback fees… These don’t only differ between payment methods, but also between payment processing methods.
To weigh your options, you need to consider the total costs of each option and consider how you might mitigate them.
For example, you could consider factoring card transaction fees into the pricing of your products upfront.
Alternatively, you could notify the customer about additional fees associated with a particular payment method and let them decide how to proceed.
5. Ensure a User-Friendly Experience
Adding extra steps to the customer journey only makes sense when it helps maintain optimal safety. But, aside from security protocols, you can’t risk sending your customers on any detours.
Simple barriers such as incomplete cost information or lack of filtering can distract customers or discourage them from buying altogether.
Below are some simple things you can do that facilitate a positive user experience, regardless of your chosen payment method:
- Make shipping costs known already on the product pages by guiding customers to create a profile or pick a shipping location (Amazon is a good example)
- Create disclaimers explaining if additional fees may be charged before the checkout
- Display the prices in the customers’ local currency
- Specify if a discount code or product line is only available in a certain region to avoid disappointments at the checkout
- Provide adequate sorting and filtering options to help customers find suitable items fast (for example, setting a price limit, or viewing in order from least to most expensive item)
6. Adapt to Local Rules and Preferences
We’ve established that payment localization is an important step to unlocking the full potential of any customer base.
It’s a way to show you know them and are choosing to support their varied preferences, needs, and habits.
These are the localization steps you can follow regardless of your logistics:
- Research your list of target markets, their payment preferences, and their behavior trends
- Narrow down your options to relevant payment channels
- Find any common denominators between target markets, for example, their shared preference for PayPal
- Make tradeoffs, and end up with a set of payment methods you can offer sustainably
- Monitor how much each payment channel is used so you can adjust course in the future
The Future of eCommerce Payment Methods

As an eCommerce business, your future success hinges on these key factors:
- Localization
- Competitive edge
- Security
Offering only one or two payment methods isn’t enough, especially for an international audience. You need a bigger pool of payment methods to stay competitive, as well as cater to multiple target markets.
However, with the rise of digital payments, we are already seeing higher security risks.
Cyber threats are becoming more sophisticated. It’s enough for an employee to open a link in an email to open the door for a data breach.
You need to ensure you’re implementing layers of security measures to mitigate the risks, run your business sustainably, and justify your customers’ trust.
Online Payment Methods: Summary

Offering multiple payment methods is necessary for all eCommerce businesses. It’s a way to give customers more control over their payments and ensure everyone can find a suitable option.
This raises the odds of more customers completing the checkout process, thus lowering cart abandonment rates, and encouraging repeat purchases for you.
If you have further questions about online payment methods, or you’re ready to partner with a payment services provider and integrate them all in one platform, feel free to contact KOMOJU.

We help businesses accept payments online.


















